> Antigen, Antibodies, ELISA, Western Blot > Primary Antibody > Polyclonal Antibodies > HAP1 Antibody (Internal)Brand |
Leading Biology | Catalog Number |
APR12326G |
Product Type |
Polyclonal Antibodies | Field of Research |
|
Product Overview |
We constantly strive to ensure we provide our customers with the best antibodies. As a result of this work we offer this antibody in purified format.
We are in the process of updating our datasheets. If you have any questions regarding this update, please feel free to contact our technical support team.
This product is a high quality HAP1 antibody (Internal).
|
||
Molecular Weight |
76kDa
|
||
Cellular Localization |
Antigen Cellular Localization:
Cytoplasm. Cell projection, axon. Cytoplasm, cytoskeleton. Lysosome. Endoplasmic reticulum. Cytoplasmic vesicle, secretory vesicle, synaptic vesicle. Mitochondrion. Nucleus. Cytoplasmic vesicle, autophagosome. Note=Localizes to large nonmembrane-bound cytoplasmic bodies found in various types of neurons, called stigmoid bodies (STBs). Localization to neuronal processes and neurite tips is decreased by YWHAZ. In the nucleus localizes to nuclear rods (By similarity).
|
||
Host |
Goat
|
||
Species Reactivity |
Human
|
||
Target |
Human HAP1. This antibody is expected to recognize all reported isoforms (NP_003940.1, NP_817084.1)
|
||
Symbol |
HAP2, HLP1
|
||
GeneID |
|||
UniProt ID |
|||
Function |
Originally identified as neuronal protein that specifically associates with HTT/huntingtin and the binding is enhanced by an expanded polyglutamine repeat within HTT possibly affecting HAP1 interaction properties. Both HTT and HAP1 are involved in intracellular trafficking and HAP1 is proposed to link HTT to motor proteins and/or transport cargos. Seems to play a role in vesicular transport within neurons and axons such as from early endosomes to late endocytic compartments and to promote neurite outgrowth. The vesicular transport function via association with microtubule-dependent transporters can be attenuated by association with mutant HTT. Involved in the axonal transport of BDNF and its activity-dependent secretion; the function seems to involve HTT, DCTN1 and a complex with SORT1. Involved in APP trafficking and seems to faciltate APP anterograde transport and membrane insertion thereby possibly reducing processing into amyloid beta. Involved in delivery of gamma- aminobutyric acid (GABA(A)) receptors to synapses; the function is dependent on kinesin motor protein KIF5 and is disrupted by HTT with expanded polyglutamine repeat. Involved in regulation of autophagosome motility by promoting efficient retrograde axonal transport. Seems to be involved in regulation of membrane receptor recycling and degradation, and respective signal transduction, including GABA(A) receptors, tyrosine kinase receptors, EGFR, IP3 receptor and androgen receptor. Among others suggested to be involved in control of feeding behavior (involving hypothalamic GABA(A) receptors), cerebellar and brainstem development (involving AHI1 and NTRK1/TrkA), postnatal neurogenesis (involving hypothalamic NTRK2/TrkB), and ITPR1/InsP3R1-mediated Ca(2+) release (involving HTT and possibly the effect of mutant HTT). Via association with DCTN1/dynactin p150-glued and HTT/huntingtin involved in cytoplasmic retention of REST in neurons. May be involved in ciliogenesis. Involved in regulation of exocytosis. Seems to be involved in formation of cytoplasmic inclusion bodies (STBs). In case of anomalous expression of TBP, can sequester a subset of TBP into STBs; sequestration is enhanced by an expanded polyglutamine repeat within TBP. HAP1-containing STBs have been proposed to play a protective role against neurodegeneration in Huntigton disease (HD) and spinocerebellar ataxia 17 (SCA17).
|
||
Summary |
Originally identified as neuronal protein that specifically associates with HTT/huntingtin and the binding is enhanced by an expanded polyglutamine repeat within HTT possibly affecting HAP1 interaction properties. Both HTT and HAP1 are involved in intracellular trafficking and HAP1 is proposed to link HTT to motor proteins and/or transport cargos. Seems to play a role in vesicular transport within neurons and axons such as from early endosomes to late endocytic compartments and to promote neurite outgrowth. The vesicular transport function via association with microtubule-dependent transporters can be attenuated by association with mutant HTT. Involved in the axonal transport of BDNF and its activity-dependent secretion; the function seems to involve HTT, DCTN1 and a complex with SORT1. Involved in APP trafficking and seems to faciltate APP anterograde transport and membrane insertion thereby possibly reducing processing into amyloid beta. Involved in delivery of gamma- aminobutyric acid (GABA(A)) receptors to synapses; the function is dependent on kinesin motor protein KIF5 and is disrupted by HTT with expanded polyglutamine repeat. Involved in regulation of autophagosome motility by promoting efficient retrograde axonal transport. Seems to be involved in regulation of membrane receptor recycling and degradation, and respective signal transduction, including GABA(A) receptors, tyrosine kinase receptors, EGFR, IP3 receptor and androgen receptor. Among others suggested to be involved in control of feeding behavior (involving hypothalamic GABA(A) receptors), cerebellar and brainstem development (involving AHI1 and NTRK1/TrkA), postnatal neurogenesis (involving hypothalamic NTRK2/TrkB), and ITPR1/InsP3R1-mediated Ca(2+) release (involving HTT and possibly the effect of mutant HTT). Via association with DCTN1/dynactin p150-glued and HTT/huntingtin involved in cytoplasmic retention of REST in neurons. May be involved in ciliogenesis. Involved in regulation of exocytosis. Seems to be involved in formation of cytoplasmic inclusion bodies (STBs). In case of anomalous expression of TBP, can sequester a subset of TBP into STBs; sequestration is enhanced by an expanded polyglutamine repeat within TBP. HAP1-containing STBs have been proposed to play a protective role against neurodegeneration in Huntigton disease (HD) and spinocerebellar ataxia 17 (SCA17).
|
||
Form |
Liquid |
||
Storage & Stability |
Store at +4°C short term. For long-term storage, aliquot and store at -20°C or below. Stable for 12 months at -20°C. Avoid repeated freeze-thaw cycles.
|
||
Applications |
WB, IHC-P, E
|
||
Dilution |
ELISA (1:32000), IHC-P (3.75 μg/ml), WB (0.1 μg/ml)
|
||
Synonyms |
Huntingtin-associated protein 1, HAP-1, Neuroan 1, HAP1, HAP2, HLP1
|
||
Images |

Antibody (0.1 ug/ml) staining of Human Brain (Hippocampus) lysate (35 ug protein in RIPA buffer). 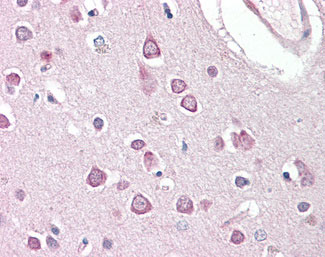
Anti-HAP1 antibody IHC of human brain, cortex. |
||
Specification |
|||
Quantity |
|
||
| Select | Brand | Catalog No. | Product Name | Pack Size | Type | Field of Research | Specification | Quantity | Price(USD) | |
| 1 | Leading Biology | APR03440G | ITGA11 Antibody (N-term) | 100 μl | Polyclonal Antibodies |
|
$495.00 | Add Ask | ||
| 2 | Leading Biology | APR04537G | CMIP Antibody (C-term) | 100 μl | Polyclonal Antibodies |
|
$495.00 | Add Ask | ||
| 3 | Leading Biology | APR12422G | Human H4 Histamine Receptor (extracellular) Antibody | 50 μl | Polyclonal Antibodies |
|
$695.00 | Add Ask | ||
| 4 | Leading Biology | APR03844G | UBE2W Antibody (C-term) | 100 μl | Polyclonal Antibodies |
|
$495.00 | Add Ask | ||
| 5 | Leading Biology | APR04349G | HECTD2 Antibody (N-term) | 100 μl | Polyclonal Antibodies |
|
$495.00 | Add Ask | ||
| 6 | Leading Biology | APR03502G | IGHG1 Antibody (Center) | 100 μl | Polyclonal Antibodies |
|
$495.00 | Add Ask |
 Leading Biology Inc.
2600 Hilltop DR, Building G, B Suite C138
Richmond, CA, 94806
Tel: 1-661-524(LBI)-0262
Email: info@leadingbiology.com
Leading Biology Inc.
2600 Hilltop DR, Building G, B Suite C138
Richmond, CA, 94806
Tel: 1-661-524(LBI)-0262
Email: info@leadingbiology.com
Complete this form and click send to ask us a question, request a quote or simply say hello.

You have 0 item in your cart

You have 0 item in your inquiry list
