The Fc-gamma receptor (FcR), a member of the immunoglobulin superfamily, is divided into FcγRI (CD64), FcγRIIa (CD32a), FcγRIIb (CD32b), FcγRIIIa (CD16a) and FcγRIIIb (CD16b). Historically, these receptors have been classified based on their affinity for specific IgG subclasses and whether their binding initiates activation or transmits inhibition signals. The Fc-gamma receptor is expressed on many immune cells and binds to monomeric IgG with high affinity, thereby modulating the immune response.
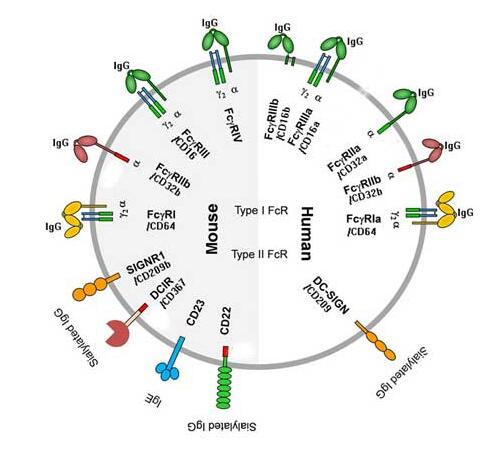
The Fc receptors are transmembrane proteins typically classified based on the class of antibody they recognize. For instance, Fc gamma receptors bind IgG, Fc epsilon Receptors bind IgE and FcR alpha binds IgA and IgM. Fc receptors are expressed by a range of immune cell types where they bind the Fc region of antibodies and modulate immune-related functions such as phagocytosis, cytolytic activity, cellular activation, and the half-life of circulating antibodies. Fc receptors are important intermediaries between the cells expressing them and antibody antigen complexes that trigger these immune responses. Because of this role, an understanding of Fc receptor function is crucial for those developing immunotherapeutic antibodies.
FC GAMMA RECEPTOR BINDING ASSAYS
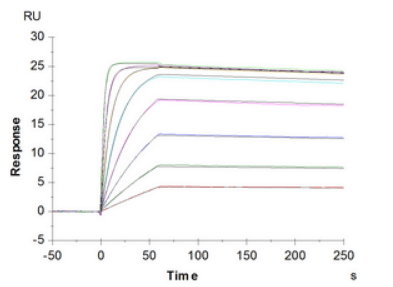
Detailed kinetic analysis of FcγR and FcRn binding to antibodies using SPR-based assays
Fc gamma receptors are a family of glycoproteins expressed on a variety of immune cells with affinity for the Fc region of immunoglobulin G (IgG). The receptor family includes several members: FcγRI (CD64), FcγRIIa/b/c (CD32a/b/c), and FcγRIIIa/b (CD16a/b) with different polymorphic variants. Each of them has characteristic preferences for the binding of IgG isotypes and can transduce either activating (e.g. FcγRI, IIa, IIIa) or inhibitory (e.g. FcγRIIb) signals. FcγRs have been shown to be important in modulating the efficacy of therapeutic mAbs by FcγR-mediated phagocytosis, cytokine production, antibody-dependent cell-mediated cytotoxicity (ADCC) and antibody-dependent cell-mediated phagocytosis (ADCP). The affinity and effector function is critically effected by the N-glycosylation profile of FcγR and antibody.
The neonatal Fc receptor (FcRn) is structurally distinct and binds to IgG within the acidic environment (pH < 6.5) of endosomes but, in contrast, not at physiological pH. FcRn enables transcytosis of IgG and mediates the half-life of IgG and therapeutic antibodies.
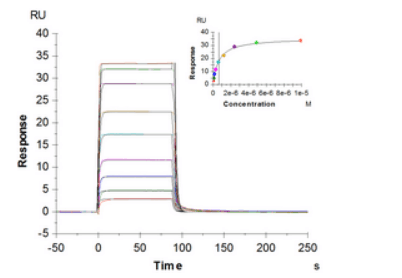
With our state-of-the-art technology and experienced scientists, Leading Biology has introduced a novel, reliable and highly flexible platform for evaluating FcγR binding properties. We can perform FcyR binding assays based on the following techniques:
For more details, please feel free to contact us or send us a query directly.
| No | Headline | Click | Author | Date |
| 1 | ScFv Phage Library Construction Service | 1201 | Leading Biology | 2020-05-27 |
| 2 | ScFv Phage Library Screening Service | 769 | Leading Biology | 2020-05-25 |
| 3 | Antibody Optimization Service | 642 | Leading Biology | 2020-05-25 |
| 4 | FcR Binding Assay Services | 1246 | Leading Biology | 2020-05-22 |
| 5 | Recombinant Antibody (IgG) Production Services | 763 | Leading Biology | 2020-05-21 |
| 6 | Recombinant Antibody (scFv) Production Services | 973 | Leading Biology | 2020-05-20 |