> Antigen, Antibodies, ELISA, Western Blot > Primary Antibody > Monoclonal Antibodies > ARNTL AntibodyBrand |
Leading Biology | Catalog Number |
AMM02759G |
Product Type |
Monoclonal Antibodies | Field of Research |
|
Product Overview |
We constantly strive to ensure we provide our customers with the best antibodies. As a result of this work we offer this antibody in purified format.
We are in the process of updating our datasheets. If you have any questions regarding this update, please feel free to contact our technical support team.
This product is a high quality ARNTL Antibody.
|
||
Molecular Weight |
68.7kDa
|
||
Cellular Localization |
Antigen Cellular Localization:
Nucleus {ECO:0000255|PROSITE- ProRule:PRU00981, ECO:0000269|PubMed:24005054}. Cytoplasm {ECO:0000250|UniProtKB:Q9WTL8}. Nucleus, PML body {ECO:0000250|UniProtKB:Q9WTL8}. Note=Shuttles between the nucleus and the cytoplasm and this nucleocytoplasmic shuttling is essential for the nuclear accumulation of CLOCK, target gene transcription and the degradation of the CLOCK-ARNTL/BMAL1 heterodimer. The sumoylated form localizes in the PML body Sequestered to the cytoplasm in the presence of ID2 {ECO:0000250|UniProtKB:Q9WTL8}
|
||
Host |
Mouse
|
||
Species Reactivity |
Human
|
||
Clone |
1C5
|
||
Isotype |
IgG1
|
||
Symbol |
BHLHE5, BMAL1, MOP3, PASD3
|
||
GeneID |
|||
UniProt ID |
|||
Function |
Transcriptional activator which forms a core component of the circadian clock. The circadian clock, an internal time- keeping system, regulates various physiological processes through the generation of approximately 24 hour circadian rhythms in gene expression, which are translated into rhythms in metabolism and behavior. It is derived from the Latin roots 'circa' (about) and 'diem' (day) and acts as an important regulator of a wide array of physiological functions including metabolism, sleep, body temperature, blood pressure, endocrine, immune, cardiovascular, and renal function. Consists of two major components: the central clock, residing in the suprachiasmatic nucleus (SCN) of the brain, and the peripheral clocks that are present in nearly every tissue and organ system. Both the central and peripheral clocks can be reset by environmental cues, also known as Zeitgebers (German for 'timegivers'). The predominant Zeitgeber for the central clock is light, which is sensed by retina and signals directly to the SCN. The central clock entrains the peripheral clocks through neuronal and hormonal signals, body temperature and feeding-related cues, aligning all clocks with the external light/dark cycle. Circadian rhythms allow an organism to achieve temporal homeostasis with its environment at the molecular level by regulating gene expression to create a peak of protein expression once every 24 hours to control when a particular physiological process is most active with respect to the solar day. Transcription and translation of core clock components (CLOCK, NPAS2, ARNTL/BMAL1, ARNTL2/BMAL2, PER1, PER2, PER3, CRY1 and CRY2) plays a critical role in rhythm generation, whereas delays imposed by post-translational modifications (PTMs) are important for determining the period (tau) of the rhythms (tau refers to the period of a rhythm and is the length, in time, of one complete cycle). A diurnal rhythm is synchronized with the day/night cycle, while the ultradian and infradian rhythms have a period shorter and longer than 24 hours, respectively. Disruptions in the circadian rhythms contribute to the pathology of cardiovascular diseases, cancer, metabolic syndromes and aging. A transcription/translation feedback loop (TTFL) forms the core of the molecular circadian clock mechanism. Transcription factors, CLOCK or NPAS2 and ARNTL/BMAL1 or ARNTL2/BMAL2, form the positive limb of the feedback loop, act in the form of a heterodimer and activate the transcription of core clock genes and clock-controlled genes (involved in key metabolic processes), harboring E-box elements (5'-CACGTG-3') within their promoters. The core clock genes: PER1/2/3 and CRY1/2 which are transcriptional repressors form the negative limb of the feedback loop and interact with the CLOCK|NPAS2-ARNTL/BMAL1|ARNTL2/BMAL2 heterodimer inhibiting its activity and thereby negatively regulating their own expression. This heterodimer also activates nuclear receptors NR1D1/2 and RORA/B/G, which form a second feedback loop and which activate and repress ARNTL/BMAL1 transcription, respectively. ARNTL/BMAL1 positively regulates myogenesis and negatively regulates adipogenesis via the transcriptional control of the genes of the canonical Wnt signaling pathway. Plays a role in normal pancreatic beta-cell function; regulates glucose-stimulated insulin secretion via the regulation of antioxidant genes NFE2L2/NRF2 and its targets SESN2, PRDX3, CCLC and CCLM. Negatively regulates the mTORC1 signaling pathway; regulates the expression of MTOR and DEPTOR. Controls diurnal oscillations of Ly6C inflammatory monocytes; rhythmic recruitment of the PRC2 complex imparts diurnal variation to chemokine expression that is necessary to sustain Ly6C monocyte rhythms. Regulates the expression of HSD3B2, STAR, PTGS2, CYP11A1, CYP19A1 and LHCGR in the ovary and also the genes involved in hair growth. Plays an important role in adult hippocampal neurogenesis by regulating the timely entry of neural stem/progenitor cells (NSPCs) into the cell cycle and the number of cell divisions that take place prior to cell-cycle exit. Regulates the circadian expression of CIART and KLF11. The CLOCK-ARNTL/BMAL1 heterodimer regulates the circadian expression of SERPINE1/PAI1, VWF, B3, CCRN4L/NOC, NAMPT, DBP, MYOD1, PPARGC1A, PPARGC1B, SIRT1, GYS2, F7, NGFR, GNRHR, BHLHE40/DEC1, ATF4, MTA1, KLF10 and also genes implicated in glucose and lipid metabolism. Represses glucocorticoid receptor NR3C1/GR-induced transcriptional activity by reducing the association of NR3C1/GR to glucocorticoid response elements (GREs) via the acetylation of multiple lysine residues located in its hinge region. Promotes rhythmic chromatin opening, regulating the DNA accessibility of other transcription factors. The NPAS2-ARNTL/BMAL1 heterodimer positively regulates the expression of MAOA, F7 and LDHA and modulates the circadian rhythm of daytime contrast sensitivity by regulating the rhythmic expression of adenylate cyclase type 1 (ADCY1) in the retina.
|
||
Storage & Stability |
Store at +4°C short term. For long-term storage, aliquot and store at -20°C or below. Stable for 12 months at -20°C. Avoid repeated freeze-thaw cycles.
|
||
Applications |
WB, IHC, E
|
||
Dilution |
WB~~1/500 - 1/2000
IHC~~1/200 - 1/1000
|
||
Images |

Figure 1: Western blot analysis using ARNTL mouse mAb against ARBTL(AA: 1-310)-hIgGFc transfected HEK293 cell lysate. 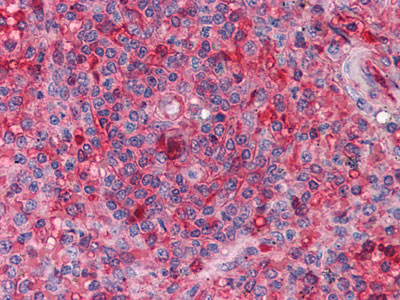
Figure 2: Immunohistochemical analysis of paraffin-embedded human Spleen tissues using anti-ARNTL mouse mAb |
||
Specification |
|||
Quantity |
|
||
| Select | Brand | Catalog No. | Product Name | Pack Size | Type | Field of Research | Specification | Quantity | Price(USD) | |
| 1 | Leading Biology | APG02467G | CCK4 / PTK7 Antibody (clone 4F9) | 50 μl | Monoclonal Antibodies |
|
$495.00 | Add Ask | ||
| 2 | Leading Biology | AMM04683G | GALT Antibody (clone 4C11) | 50 μg | Monoclonal Antibodies |
|
$545.00 | Add Ask | ||
| 3 | Leading Biology | AMM01402G | Vimentin (Mesenchymal Cell Marker) Antibody - With BSA and Azide | 50 ug | Monoclonal Antibodies |
|
$395.00 | Add Ask | ||
| 4 | Leading Biology | APR08280G | LTA4H / LTA4 Antibody (clone 9G8) | 50 μl | Monoclonal Antibodies |
|
$495.00 | Add Ask | ||
| 5 | Leading Biology | AMM00172G | CD1a / HTA1 (Mature Langerhans Cells Marker) Antibody - With BSA and Azide | 50 ug | Monoclonal Antibodies |
|
$395.00 | Add Ask | ||
| 6 | Leading Biology | AMM05750G | CEBPA Antibody | 100 μl | Monoclonal Antibodies |
|
$545.00 | Add Ask |
 Leading Biology Inc.
2600 Hilltop DR, Building G, B Suite C138
Richmond, CA, 94806
Tel: 1-661-524(LBI)-0262
Email: info@leadingbiology.com
Leading Biology Inc.
2600 Hilltop DR, Building G, B Suite C138
Richmond, CA, 94806
Tel: 1-661-524(LBI)-0262
Email: info@leadingbiology.com
Complete this form and click send to ask us a question, request a quote or simply say hello.

You have 0 item in your cart

You have 0 item in your inquiry list
