Introduction
Genotyping is the process of determining which genetic variants an individual possesses, it can be performed through a variety of different methods, depending on the variants of interest and the resources available.
SNP Genotyping Analysis
A single-nucleotide polymorphism (SNP) is sequence variation at the single-base level. They can be found in coding, non-coding, and intronic regions of genomes, and they may affect transcription factor binding, gene splicing, protein folding and many other elements at the gene and transcript level.
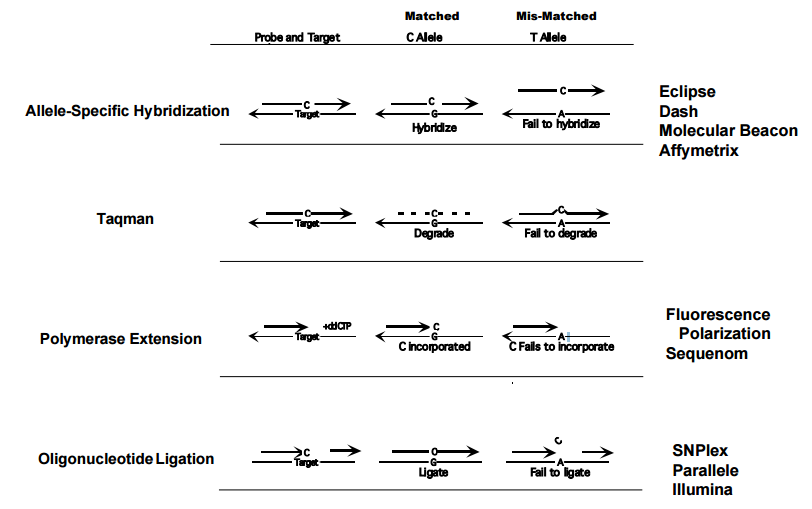
Fig. 1 SNP Genotyping methods
There are several methods for SNP genotyping, including dynamic allele-specific hybridization, Molecular bacons, PCR based methods, oligonucleotide ligation assay, etc. Typically, the genotyping protocols start with target amplification and follow with allelic discrimination and production or identification, the allelic discrimination reaction step including primer extension, pyrosequencing, ligation, structure specific cleavage and hybridization, some or all of these steps could be combined and processed in parallel. The last step is the allele specific product identification, the methods including fluorescence intensity/FRET/FP detection, Mass spectrometry detection, electrophoresis and microarry.
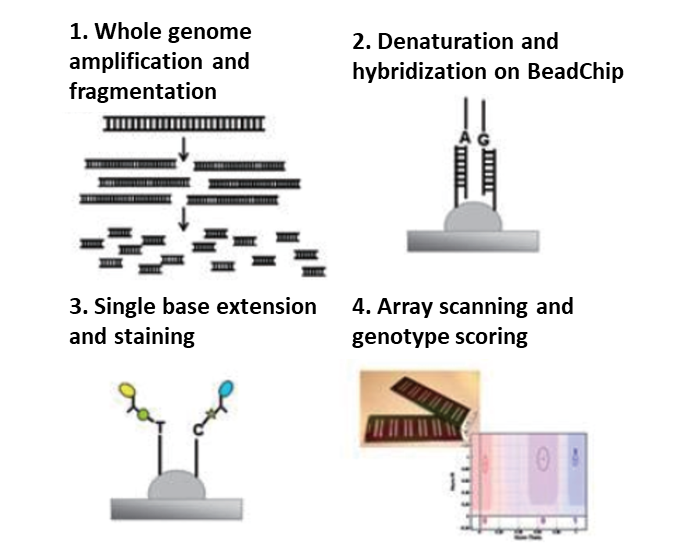
CNV Analysis
Copy Number Variations (CNVs) are a type of genomic alteration to regions of DNA, which are at least one kb in size, these alterations resulting in an abnormal copy number of specific regions that cause the physical rearrangement of genes on chromosomes. Typically, the structural genomic rearrangements such as duplications, deletions, translocations, and inversions can cause CNVs.
AFLP Genotyping Analysis
Amplified Fragment Length Polymorphisms (AFLPs) are polymerase chain reaction (PCR) based markers for the rapid screening of genetic diversity. AFLP methods rapidly generate hundreds of highly replicable markers from the DNA of any organism, thus, they allow high-resolution genotyping of fingerprinting quality. AFLP markers are high replicable and easy to use, so it’s widely used as a new type of genetic marker with broad application in systematics, pathotyping, population genetics, DNA fingerprinting and quantitative trait loci (QTL) mapping.
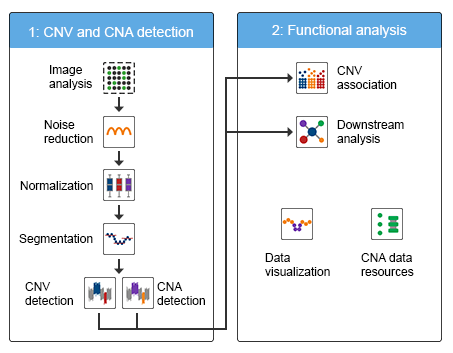
The originality of the AFLP method was to design and synthesis arbitrary primers, the primers then were ligated to target DNA fragments, the target DNA sequences are DNA fragments generated by restriction enzymes. Then, adapters were ligated at each end of a restriction fragment by a protein ligase. Finally, adapters were used in a PCR as priming sites to amplify the restriction fragments.
Fig. 4 AFLP principle
Why Leading Biology?
At Leading Biology, we custom protein purification design for every single protein to ensure the production and recovery rate as high as possible.
Working with us, you will get stability, and it means a reliable partner to help streamline your R&D process.
Working with us, you will get the guaranteed service to accommodate your requirements.
· Vigorous quality control system to ensure the required quality and reproducibility
· Competitive price with fast turnaround time
Contact Information
Please obtain a quote before ordering, and refer to the quote number when you place an order.
Orders are typically confirmed within 12 hours.
Have a Question? Email us info@leadingbiology.com
Order Products: Order Related Products
By Phone: 1-661-524(LBI)-0262 (USA)
| No | Headline | Click | Author | Date |
| 1 | siRNA/shRNA gene knockdown | 1779 | Leading Biology | 2018-01-26 |
| 2 | Tetracycline Induced Gene knockout/knockin | 1977 | Leading Biology | 2018-01-26 |
| 3 | New Generation Embryonic Stem Cells Gene Targeting | 1983 | Leading Biology | 2018-01-26 |
| 4 | TALEN Technology | 1813 | Leading Biology | 2018-01-26 |
| 5 | CRISPR-CAS Technology | 2246 | Leading Biology | 2018-01-26 |
| 6 | Microorganisms Gene Modification Services | 1711 | Leading Biology | 2018-01-26 |