> Information Center > Technical FAQs > Antibody Technology Column > Which antibodies are monomersThe simplest antibodies, such as IgG, IgD, and IgE, are "Y"-shaped macromolecules called monomers.
In this section we will look at the structure of antibodies. There are five classes or isotypes of human antibodies :
a. immunoglobulin G (IgG),
b. immunoglobulin M (IgM),
c. immunoglobulin A (IgA),
d. immunoglobulin D (IgD), and
e. immunoglobulin E (IgE).
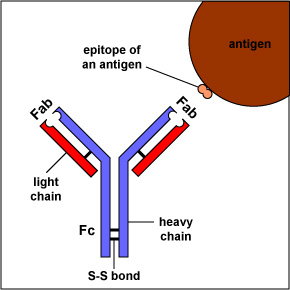
The simplest antibodies, such as IgG, IgD, and IgE, are "Y"-shaped macromolecules called monomers. A monomer is composed of four glycoprotein chains: two identical heavy chains and two identical light chains. The two heavy chains have a high molecular weight that varies with the class of antibody. The light chains come in two varieties: kappa or lambda and have a lower molecular weight than the heavy chains. The four glycoprotein chains are connected to one another by disulfide (S-S) bonds and non-covalent bonds (Figure 1).