> Information Center > Technical FAQs > Antibody Technology Column > What are the features of yeast expressionA yeast expression platform is a strain of yeast used to produce large amounts of proteins, sugars, or other compounds for research or industrial uses. While yeast is often more resource-intensive to maintain than bacteria, certain products can only be produced by eukaryotic cells like yeast, necessitating the use of a yeast expression platform. Yeasts differ in productivity and with respect to their capabilities to secrete, process and modify proteins. As such, different types of yeast (i.e. different expression platforms) are better suited for different research and industrial applications.
The various yeast expression platforms differ in several characteristics, including their productivity and with respect to their capabilities to secrete, to process and to modify proteins in particular examples. However, the uses of all expression platforms have some basic similarities.
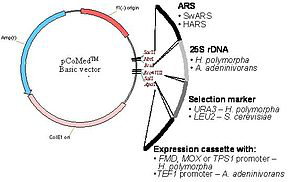
Fig. 1. Design and functionality of CoMed vector system. The CoMed basic vector contains all E. coli elements for propagation in the E. coli system and a MCS (multiple cloning ste) for integration of ARS, rDNA, selection marker and expression cassette modules. For this purpose, ARS fragments are flanked by SacII and BcuI restriction sites, rDNA regions by BcuI and Eco47III restriction sites, selection markers by Eco47III and SalI restriction sites and promoter elements by SalI and ApaI restriction sites.
In order to produce a desired product, suitable yeast strains are transformed with a vector that contains all necessary genetic elements for the production of a biological product of interest. Vectors must also contain a selection marker, which is required to select yeast which has successfully taken up the vector from those which have not. Vectors also contain certain DNA elements allowing the yeast to incorporate the foreign DNA into the chromosome of the yeast and to replicate it. Most importantly, vectors contain a segment responsible for the production of the desired compound, called an expression cassette. The cassette contains a sequence of regulatory elements that control how much and under which circumstances a certain product is eventually made. This is followed by the gene for the biological product itself. The expression cassette is terminated by a terminator sequence that stops the transcription of the expressed gene.